Discover key insights on thick anal in pets, including symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventative measures, to ensure your furry friend stays healthy and happy.
Thick anal refers to a condition that can affect pets, particularly dogs, where the anal glands may become enlarged or impacted. This condition can lead to discomfort and health issues if not addressed properly. Understanding thick anal is essential for pet owners to ensure their furry friends remain happy and healthy.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of thick anal can help in preventing potential complications. Addressing this issue promptly can lead to a healthier pet and potentially save on costly veterinary bills. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for thick anal, helping you to keep your beloved pet in great shape.
By reading this post, you will gain valuable insights into identifying thick anal and how to treat it effectively. You will discover when to consult your veterinarian and what preventive measures you can take.
Ignoring this issue could lead to severe discomfort for your pet, possible infections, and even more serious health complications that may require veterinary intervention.
Speaking of plants, the large peace lily plant is an excellent choice for indoor spaces. It not only adds beauty but also improves air quality. For more information, check out this article on the large peace lily plant benefits.
What Is Thick Anal?
Thick anal is a condition that typically affects dogs when their anal glands become swollen or impacted. This can happen for various reasons, from dietary issues to environmental factors. It’s important to know that thick anal can lead to discomfort for your pet, affecting their overall health if left untreated.
What is thick anal?
Thick anal refers to the enlargement of anal glands, which can produce discomfort and health issues for pets. Dogs with thick anal may show signs of pain, difficulty sitting, or excessive licking of the area.
How does this condition affect a pet’s overall health?
This condition can lead to infections if the anal glands are not functioning properly. In severe cases, it may require surgical intervention. Keeping an eye on your pet’s behavior can help catch this issue early.
What’s the difference between mild and severe cases?
Mild cases may only cause slight discomfort and can often be treated at home, while severe cases can lead to infections and require veterinary attention. For example, a dog that occasionally scoots may have a mild case, but one that is lethargic and refuses to eat may be facing a severe issue.
Are there different types or categories of this condition?
Thick anal can be categorized into acute and chronic cases. Acute cases arise suddenly and may resolve quickly, while chronic cases can be long-lasting and require ongoing care.
What are the medical or scientific terms for this condition?
The medical term for issues related to thick anal is “anal sac disease” or “anal sac impaction.” Understanding these terms can help when discussing your pet’s health with a veterinarian.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Common signs of thick anal can include scooting, excessive licking of the anal area, and difficulty sitting. Observing these behaviors can help you identify the problem early on and seek the necessary treatment.
What physical signs should pet owners look for?
- Scooting or dragging their rear on the ground
- Excessive licking of the anal area
- Signs of pain or discomfort when sitting
How do symptoms vary by breed or size of pet?
Some breeds, like Cocker Spaniels and Bulldogs, are more prone to thick anal due to their anatomical structure. Smaller dogs may have more noticeable symptoms due to their size, making it easier for owners to detect issues.
Are the symptoms seasonal or constant?
Symptoms can be constant but may worsen during allergy seasons. Environmental factors can play a role in the severity of the symptoms experienced by your pet.
Can this condition affect behavior or mood?
Yes, pets suffering from thick anal may become irritable or withdraw from activities they usually enjoy. For example, a normally playful dog may become less active, indicating discomfort.
Are there symptoms that are easy to miss?
Some symptoms, like slight changes in appetite or minor scooting, can be easy to overlook. Regularly monitoring your pet’s behavior can help catch these subtle signs.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with thick anal is crucial for prevention. Factors include diet, environment, and genetics. By addressing these factors, pet owners can help reduce the risk of their pets suffering from this condition.
What are the most common causes of this condition?
The most common causes include poor diet, lack of fiber, and obesity. For example, a diet lacking in fiber may lead to insufficient natural expression of anal glands, leading to impaction.
Are environmental factors (climate, air quality) contributing?
Yes, poor air quality and allergens can worsen symptoms. A pet living in a dusty environment may experience more irritation and swelling.
Can poor diet or nutrition lead to this issue?
Absolutely. A diet low in fiber can prevent proper anal gland function, leading to thick anal. For instance, dogs fed primarily processed food may face higher risks.
Which breeds are most prone to this problem?
Breeds such as Basset Hounds and Dachshunds are often more susceptible to thick anal due to their anatomy. These breeds may require extra care to prevent issues.
Are some pets genetically predisposed?
Yes, certain breeds are genetically predisposed to thick anal. It’s essential for owners of these breeds to be vigilant about their pet’s anal health.
Does age or lifestyle affect the risk?
Older pets or those with a sedentary lifestyle may be at a higher risk as they may not naturally express their anal glands as frequently, increasing the chance of impaction.
In summary, thick anal can be influenced by various factors, and understanding these can help you keep your pet healthy.
Diagnosis: How Vets Identify the Problem
When diagnosing thick anal, veterinarians will typically perform a physical examination and may use additional tools to assess the condition. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment.
How does a vet diagnose this condition?
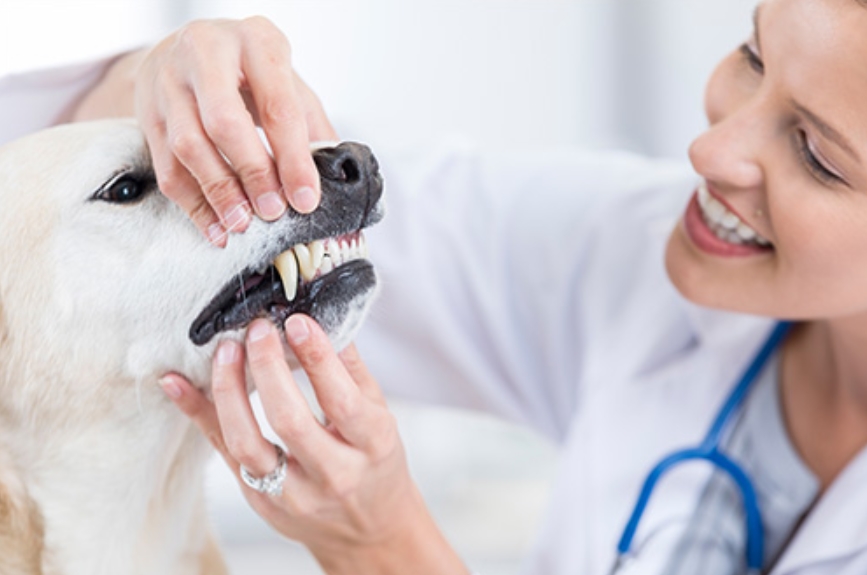
A veterinarian will perform a physical exam, checking for swelling or tenderness around the anal glands. They may also ask about your pet’s symptoms and behavior.
What tests or tools are commonly used?
Vets may use ultrasound or imaging to assess the condition of the anal glands. These tools can help identify any blockages or infections.
Can pet owners detect it at home?
While some signs may be noticeable at home, such as scooting, it’s crucial to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis. Vets have the necessary tools and expertise to assess the issue thoroughly.
What conditions must be ruled out?
It’s essential to rule out other conditions, such as infections or tumors, that may mimic symptoms of thick anal. A comprehensive examination can help ensure an accurate diagnosis.
How long does diagnosis usually take?
Diagnosis can vary but typically takes a few hours to a day, depending on the complexity of the case and tests needed.
What can go wrong if it’s misdiagnosed?
Misdiagnosis can lead to inadequate treatment and worsening of the condition. For example, if an infection is overlooked, it may result in severe health complications for your pet.
Treatment Options
Treating thick anal involves a multi-faceted approach, including at-home treatments, dietary adjustments, and veterinary medications. Understanding these options can help you choose the best path for your pet.
a. At-Home Treatments
At-home treatments can be effective in managing mild cases of thick anal. Regular grooming and monitoring can help alleviate some symptoms.
What natural remedies can help?
Some natural remedies include warm compresses to soothe the area and increase circulation. Additionally, adding fiber to your pet’s diet can help with anal gland expression.
Which shampoos, oils, or creams are recommended?
Veterinarians may recommend specific medicated shampoos or creams that can help soothe inflammation. Always consult your vet before using new products.
Are there safe DIY treatments?
Yes, some safe DIY treatments include warm baths and gentle cleaning of the anal area to prevent infections. However, always ensure your pet is calm during this process.
How often should treatments be applied?
Frequency will depend on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may only need treatment once a week, while more severe cases may require daily attention. Consult your vet for a tailored plan.
b. Dietary Adjustments
Dietary changes can play a significant role in preventing thick anal. Ensuring your pet has a balanced diet is crucial for their overall health.
Which nutrients improve skin or ear health?
Omega-3 fatty acids are excellent for improving skin health and can help reduce inflammation. Foods rich in fiber can also aid in proper anal gland function.
Are there supplements that work?
Supplements like probiotics can improve gut health and may help reduce anal gland issues. Always consult your vet before starting any supplements.
Should certain foods be avoided?
Processed foods and those high in fillers should be avoided as they can contribute to obesity and anal gland issues. Focus on high-quality, protein-rich diets.
How can an elimination diet help identify the cause?
Elimination diets can help identify food allergies that may contribute to thick anal. By gradually reintroducing foods, you can pinpoint any triggers.
Incorporating more fiber into your pet’s diet can help prevent issues with thick anal in the future.
c. Veterinary Medications
In more severe cases, veterinary medications may be necessary. Your vet can prescribe treatments to help manage thick anal effectively.
What are the most effective vet-prescribed treatments?
Commonly prescribed treatments include antibiotics for infections and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling. Your vet will guide you on the best options.
Are antibiotics or antifungals needed?
Depending on the condition, antibiotics may be necessary if an infection is present. Always follow your vet’s recommendations regarding medications.
What are the potential side effects of these medications?
Side effects can vary, but some pets may experience gastrointestinal upset or fatigue. Monitor your pet closely after starting any new medications.
How long does treatment usually last?
Treatment duration can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the severity of thick anal and the response to treatment. Regular follow-ups with the vet are essential.
Preventative Measures
Taking preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of thick anal in pets. Regular grooming, diet, and environmental factors all play a role in maintaining your pet’s health.
How can this condition be avoided in the future?
Regularly expressing your pet’s anal glands can help prevent thick anal. Routine check-ups with your veterinarian can also help catch any potential issues early on.
What daily or weekly routines help?
Establishing a grooming routine that includes checking your pet’s anal area can help identify problems before they worsen. Regular exercise also contributes to overall health.
Should pet owners change grooming habits?
Changing grooming habits to include regular checks of the anal area can help catch issues early. Make this a part of your pet’s regular grooming routine.
Does indoor air humidity or temperature play a role?
Yes, maintaining a comfortable environment can help prevent skin irritation, which may contribute to thick anal. Keep your home at a comfortable temperature and humidity level.
What products help prevent recurrence?
Using high-quality pet food that supports digestive health can help prevent recurrence. Additionally, consult your vet for specific products that may be beneficial.
Can early signs be stopped before becoming a bigger issue?
Yes, addressing early signs promptly can prevent thick anal from developing into a more severe condition. Regular monitoring and prompt veterinary care are key.
By incorporating these preventative measures, you can help keep your pet healthy and happy, reducing the risk of thick anal.
When to See a Vet
Knowing when to consult a veterinarian can make a significant difference in your pet’s health. Timely intervention can prevent complications associated with thick anal.
What symptoms indicate an emergency?
Emergency symptoms include severe pain, bleeding, or signs of infection. If your pet appears lethargic or unresponsive, seek veterinary care immediately.
How can pet owners distinguish between minor vs. serious issues?
Minor issues may include slight scooting, while serious issues could involve severe pain or refusal to eat. Understanding your pet’s normal behavior can help you identify concerning changes.
How quickly should a vet be consulted after noticing symptoms?
If you notice any symptoms of thick anal, consult your vet as soon as possible. Early intervention can prevent complications and lead to a better outcome for your pet.
Can delays cause long-term damage?
Yes, delays in seeking treatment can lead to severe complications such as infections or abscesses, which may require surgical intervention. Prompt attention is crucial.
Case Studies / Real-Life Examples
Real-life examples can provide valuable insights into managing thick anal effectively. Learning from others’ experiences can help pet owners better understand this condition.
What’s a real success story of treatment and recovery?
One dog owner noticed their pet scooting excessively. After consulting a vet, they learned their dog had thick anal. With dietary adjustments and routine vet visits, the condition improved significantly.
How did one owner recognize and manage the issue?
The owner recognized changes in their dog’s behavior, including discomfort during walks. They promptly consulted their vet, leading to a successful treatment plan that included dietary changes and regular check-ups.
What were the challenges during treatment?
One challenge faced by an owner was getting their pet to accept dietary changes. However, with patience and gradual adjustments, the pet adapted, leading to improved health.
What lessons can be learned from this experience?
The experience taught owners the importance of vigilance and early intervention. Regular monitoring and prompt veterinary care can make a significant difference in managing thick anal.
Another condition that may concern pet owners is feline scabs, which also requires attention and care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is thick anal and how can it be treated?
Thick anal is a condition where a pet’s anal glands become impacted or swollen. Treatment can include dietary changes, at-home care, and veterinary intervention. Regular vet check-ups are essential to manage this condition effectively.
How often should I check my pet for signs of thick anal?
Regular checks should be a part of your grooming routine. Aim to check your pet’s anal area at least once a week, paying attention to any signs of discomfort or irritation.
Can thick anal be prevented entirely?
While it may not be possible to prevent thick anal entirely, you can significantly reduce the risk by maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and routine veterinary care.
What are the long-term effects of untreated thick anal?
Untreated thick anal can lead to severe health issues, including infections or abscesses that may require surgical intervention. Regular monitoring and treatment can prevent these complications.
Are there specific breeds more prone to thick anal?
Yes, breeds like Cocker Spaniels, Bulldogs, and Basset Hounds are more susceptible to thick anal issues. Owners of these breeds should be particularly vigilant in monitoring their pets’ anal health.
In conclusion, understanding thick anal is crucial for pet owners. By recognizing the signs, seeking timely veterinary care, and implementing preventive measures, you can help ensure your pet remains healthy and happy.
Taking action to address thick anal is key to your pet’s well-being. Stay informed and proactive to ensure your furry friend enjoys a happy, healthy life!
Recommended Next Steps
To effectively manage and prevent thick anal in your pet, consider the following steps:
- Regular veterinary check-ups to monitor anal health.
- Incorporate high-fiber foods into your pet’s diet.
- Monitor your pet’s behavior for any signs of discomfort.
- Establish a grooming routine that includes checking the anal area.
- Consult your vet before introducing new foods or supplements.
For more insights, check out PetMD and AKC for additional information related to thick anal and pet health.
Expand Your Knowledge
- 📌 Healthy Happy Dog
- 📌 Cat Care Guide
- 📌 All About Birds
- 📌 Pigeon Care Guide
- 📌 Playful Ferret Tips
- ————————–
- 📌 Indoor Plants
- 📌 Low Light Lover Indoor Plants
Watch this helpful video to better understand thick anal:
The video focuses on providing financial advice aimed at helping individuals manage their money better and make informed financial decisions. The speaker emphasizes the importance of being mindful of spending habits and developing a solid understanding of budgeting. They suggest that individuals should take the time to analyze their income and expenses to create a comprehensive budget that aligns with their financial goals. The advice includes tips on tracking daily expenses, identifying unnecessary spending, and prioritizing savings. By sharing personal anecdotes and practical strategies, the speaker aims to motivate viewers to take charge of their financial situation and work towards building a stable and secure future.
In addition to budgeting, the speaker discusses the significance of investing and the long-term benefits it can provide. They highlight various investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, explaining how they can help grow wealth over time. The speaker encourages viewers to educate themselves about the different types of investments and to start small, gradually increasing their investment as they become more comfortable. The overall message is to not only save money but also to make that money work for you through smart investments. By following these financial principles, individuals can achieve greater financial stability and prepare for unforeseen challenges, ultimately leading to a more secure and fulfilling life.
In other news, did you know that chocolate is bad for cats? While it may be a delicious treat for humans, it can be toxic to our feline friends. Chocolate contains substances like theobromine and caffeine, which can cause serious health issues in cats, including vomiting, diarrhea, increased heart rate, and even seizures in severe cases. It’s essential for cat owners to be aware of the dangers of chocolate and to keep it out of reach from their pets. For more information on this topic, you can read our detailed post on chocolate bad for cats.
YouTube Video Library: Related Videos
Here’s the reality of anal sex (no matter what porn might teach you)!
Big ass latina milf
thick big booty brownskin | @ceetheworldd2
big ass big booty 18 #shorts
Five tips for butthole play #analsex #analplay #education
innocent big ass
big booty twerk #viral #tiktok #bigbank #miss#shetty #trending #shorts
Note: The video above is embedded from YouTube and is the property of its original creator. We do not own or take responsibility for the content or opinions expressed in the video.